What Are The Units Of Specific Heat
What Are The Units Of Specific Heat. It is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kg of liquid or solid by 1 k in si units. The unit of specific heat is:
These two forms of energy, heat and light, are essential to our existence. How the heat transfer process works between two objects is contingent on the substance it is made of and the way it is put. Radiation, convection, and energy transfer are the main methods of exchange of heat.
Transfer of energyEnergy transfer generally refers to the exchange of energy between two or more items. The possibility exists to transfer energy from one location to another, or between two objects. There are many reasons that energy transfers occur that include heating objects, or transfer of energy to the environment. This is a vital process that affects all the life forms on Earth.
Two ways energy can be transferred are through conduction and radiation. Conduction is among the most efficient methods for heat transfer in metals. One example is that the handle of a steel spoon can conduct heat efficiently. If the spoon is heated the handle will heat up.
Radiation, which is a form of energy transfer, is vital to the life of all living things on Earth. If a fire breaks out, a lot of energy is transferred into the air. The air travels at a high speed. This energy can travel all over the world.
Latent heat and sensible heatEnergy moves through space, regardless of whether it's either sensual or latent heat. It is based on the air temperature. It could also be caused by direct conduction. The energy needed to raise or lower the temperature of water is a classic example.
The energy needed to cause an alteration in the phase of a substance is known as sensible heat. Sensible heat can be required in numerous situations, including cooling and heating water.
The two main elements of any system that controls climate are latent heat and sensible heat. They play a significant role in weather, climate and oceanic phenomena.
The sensible and latent heat are assisted by the water vapor and air within the atmosphere. Water vapor is a significant greenhouse gas, which plays a part in the formation of clouds. The atmosphere is full of water vapor, which wants to rise and form clouds. The vapor is condensed when air cannot hold any more water vapor , and then releases its heat.
ConductionWhen you iron your clothes, cooking food in a kitchen stove, or simply boiling water, you are using the method of transfer of heat called conduction. Conduction of heat, one of the three main ways to transfer heat, is the other.
Conduction is a term used to describe a method by which heat is transferred through a solid, liquid or gas. It is influenced by temperature and distance traveled with the length of the journey as well as the properties of the material. The main factor in conduction is the conductivity of the temperature. This is the capacity of a substance or substance to transfer heat energy. The units used to measure thermal conductivity are Wm-1K-1.
The speed that electrons move from one atom or another is the determinant of a conductivity of the substance's thermal. It is also a measurement of how well the substance conducts electricity. Good thermal conductivity objects absorb heat more efficiently than others. The objects that have low thermal conductivity are referred to as insulators.
ConvectionConvection is an efficient way to heat and cool. The flow rate and the shape of the fluid are two aspects which influence the convection process of heat transfer. It is important that you remember that the rate of heat convection is transferred is proportional to the difference in temperatures of the fluid.
The first law of thermodynamics says that the rate of loss of heat is a function of temperature. This implies that heat is lost faster when a heated object is in contact with it would be from cold objects. Here's an example of this idea: Let's say you've got a glass filled with hot liquid and red food dye. As the water coolsdown, dye will settle and it will turn clear.
RadiationRadiation can be seen in light, heat, or both. Thermal radiation is simply the emission of heat the form of cold and heat by matter particles. It can also be defined as electromagnetic waves created by matter in its most advanced form. In certain instances, the wavelength of thermal radiation is proportional to its temperature. Infrared radiation is the most well-known form of radiation related to heat. It can be captured using an infrared camera. It can also be induced through conduction of heat. Convection is the most popular illustration. This is also a characteristic of chemistry that is based on heat.
It is easiest to visualize the intensity of the radiation's thermal spectrum by looking at its spectral component in the context a total volume of matter. It is a black hole if it doesn't have a corresponding volume.
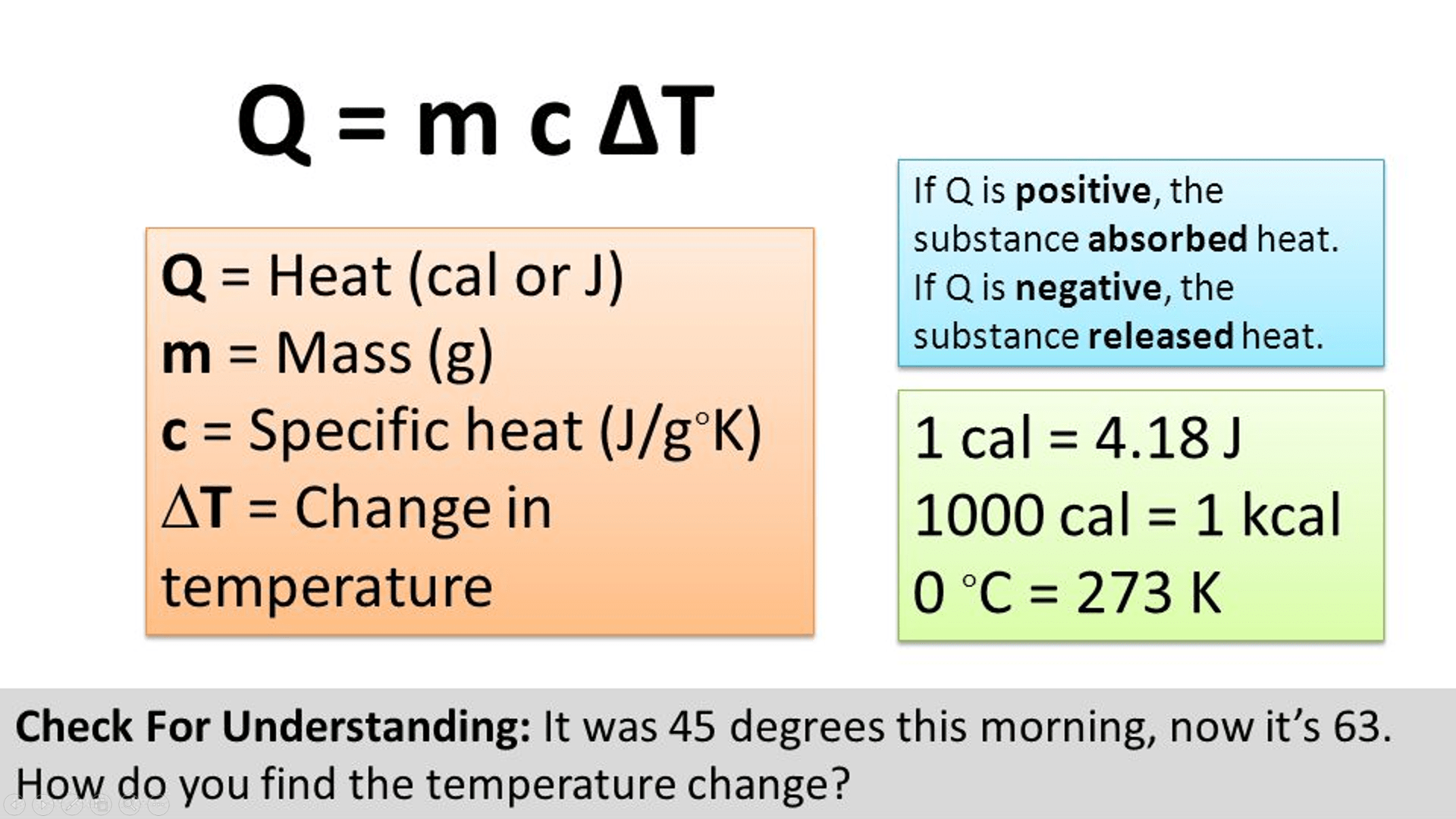
It is the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of 1 kg of liquid or solid by 1 k in si units. In si, the specific heat of a solid (or liquid) may be defined as amount of the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the solid (or liquid) through 1 k (or 1 o c) ∴ specific heat = m δ. It is denoted by c or s.
Specific Heat Capacity, C = Q M ∆ T, Where M Is The Mass Of Substance, Q Is Heat Absorbed, And ∆ T Is The Change In Temperature.
Si unit of specific heat capacity. A cal ∘c b cal/g ∘c c cal/g d cal easy solution verified by toppr correct option is b) the correct answer is option (b). The units of specific heat are is
Joule Is The Si Unit Of Heat.
[1] for example, the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1 k is 4184 joules, so. The amount of heat per one gram of a substance required to raise its temperature by 1 k (or 1 ∘ ^\circ ∘ c) is the specific heat of a substance. It may also be expressed as j/kg·k.
Formula Of Specific Heat Capacity:
4,200 j/ (kg·k) water vapor: The heat associated with the change in temperature of a material is given by q = mcδt q = m c δ t, where m m is the mass of the material, c c is the specific heat, and δt δ t is the change in. Energy / (∆temperature mass) this is related to the units of heat capacity which isn’t normalized to mass:
Specific Heat Capacity (C) Is Measured In Joules Per Kilogram Per Degree Celsius (J/Kg°C) Temperature Change (∆Θ) Is Measured In Degrees Celsius (°C) Example Sadie Is Experimenting.
The units are often joules per gram. In si, the specific heat of a solid (or liquid) may be defined as amount of the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of the solid (or liquid) through 1 k (or 1 o c) ∴ specific heat = m δ. C) is the amount of heat in joules required to raise 1 gram of a substance 1 kelvin.
Each Substance Has Their Own Specific Heat Capacity,.
The specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of heat (j) absorbed per unit mass (kg) of the material when its temperature increases 1 k (or 1 °c), and its units are j/ (kg k) or j/ (kg °c). The si unit of specific heat capacity is joule per kelvin per kilogram, j⋅kg −1 ⋅k −1. It is denoted by c or s.
Post a Comment for "What Are The Units Of Specific Heat"